Revolutionising
total hip arthroplasty
total hip arthroplasty
We combine meticulous surgical planning with decades of specialist expertise to restore your mobility faster, safer, and with greater precision.
Powered by Advanced Techniques
We utilise the latest minimally invasive and muscle-sparing protocols to ensure faster recovery and optimal implant longevity.

Minimally invasive direct anterior approach focusing on cosmetic incision and rapid rehabilitation.

Posterior approach preserving external rotators for enhanced joint stability and natural movement.
Not sure which is right for you? Free Discovery Call
Bespoke private hip replacement
Renowned as London’s ‘go-to surgeon’ for hip replacement, Professor Lee combines evidence-based methods with meticulous technique to kickstart your recovery.
With a focus on careful planning and clear communication, he sources internationally acclaimed implants designed to reduce tissue irritation. His approach ensures improved range of motion and joint stability, often resulting in rapid recovery with no post-surgical restrictions.
- Creator of the Rapid Biological Recovery® programme
- Specialist in BIKINI and SPAIRE muscle-sparing techniques
- Harley Street heritage with access to leading private surgical facilities
- Exclusive care pathway at Lincolnshire Hip Clinic

We are Committed to Excellence
World-Class Technology
Advanced imaging, pre-operative planning, and precision instrumentation for reliable surgical accuracy.
Expert Consultant
Led by Professor Lee, a specialist focused exclusively on hip preservation and replacement.
Personalised & Precise
Tailored treatment plans designed around your specific anatomy and lifestyle goals.
Double Board-Certified
Recognised excellence with certifications ensuring the highest standards of medical care.
Evidence-Based
Treatments grounded in the latest clinical research to minimise tissue damage.
Comprehensive Service
A seamless care pathway from initial diagnosis through to full rehabilitation.
Patient Stories
"Having a new hip from Professor Lee was the best thing that happened to me in 2021! It restored life to normality. Patient care from the first consultation to post-operative recovery has been second to none and clinic staff have regularly enquired about my progress. I know that in time I will need the second new hip and I have total confidence and trust in Professor Lee and his team."
"Professor Lee’s passion for surgical excellence and continued improvement were obvious, as was his attention to my needs. Ten days after the consultation... I could start to live again. His skill was evident in the complete removal of my previous pain, a short and neat scar with absolutely no bruising, all of which I found remarkable."
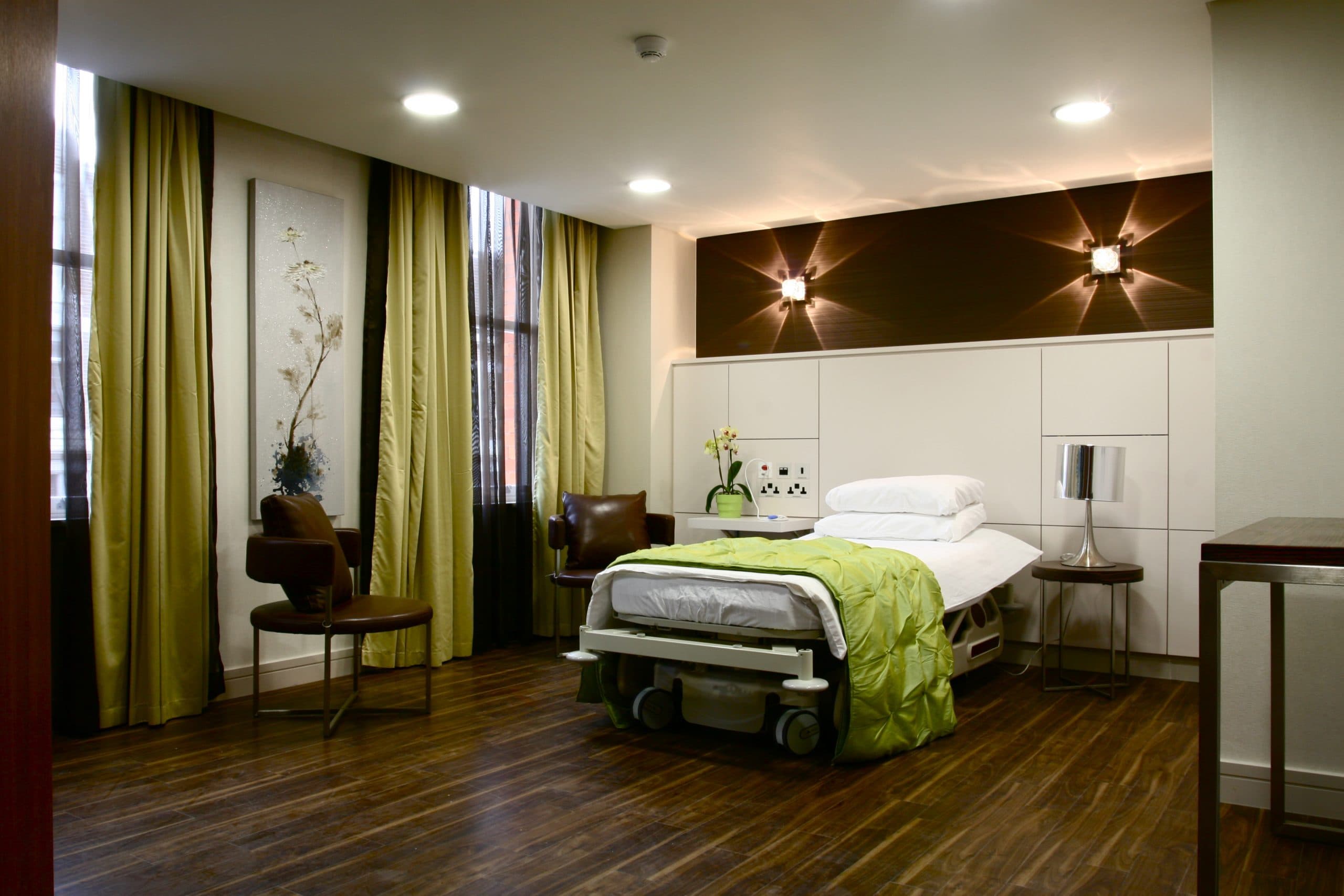

Locations
World-class surgical facilities met with convenient local care.
Surgery in Central London
We carry out our surgeries in the private Weymouth Street Hospital, Harley Street. It is widely recognised as one of the UK’s most luxurious independent hospitals, providing first-class healthcare environments.
Consultations & Aftercare
All consultations and pre- and post-op care are carried out in our private clinics in Lincolnshire:
